Table of contents
- 1. Intro to Stats and Collecting Data55m
- 2. Describing Data with Tables and Graphs1h 55m
- 3. Describing Data Numerically1h 45m
- 4. Probability2h 16m
- 5. Binomial Distribution & Discrete Random Variables2h 33m
- 6. Normal Distribution and Continuous Random Variables1h 38m
- 7. Sampling Distributions & Confidence Intervals: Mean1h 3m
- 8. Sampling Distributions & Confidence Intervals: Proportion1h 12m
- 9. Hypothesis Testing for One Sample1h 1m
- 10. Hypothesis Testing for Two Samples2h 8m
- 11. Correlation48m
- 12. Regression1h 4m
- 13. Chi-Square Tests & Goodness of Fit1h 20m
- 14. ANOVA1h 0m
4. Probability
Complements
Problem 4.r.8
Textbook Question
In Exercises 1–10, use the data in the accompanying table and express all results in decimal form. (The data are from “The Left-Handed: Their Sinister History,” by Elaine Fowler Costas, Education Resources Information Center, Paper 399519.)
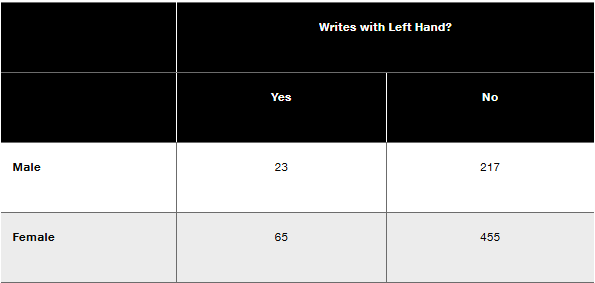
Complement If L represents the event of randomly selecting one of the study subjects and getting someone who writes with their left hand, what does L represent? Find the value of P(L)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the problem. The event L represents selecting a study subject who writes with their left hand. The complement of L, denoted as L', represents selecting a study subject who does NOT write with their left hand. We need to calculate P(L), the probability of event L occurring.
Step 2: Identify the total number of study subjects. Add all the values in the table: Total = (23 + 217) for males + (65 + 455) for females.
Step 3: Identify the number of subjects who write with their left hand. Add the values in the 'Yes' column: Left-handed total = 23 (males) + 65 (females).
Step 4: Calculate the probability of event L, P(L). Use the formula for probability: P(L) = (Number of left-handed subjects) / (Total number of subjects).
Step 5: Express the result in decimal form. Divide the left-handed total by the overall total and ensure the result is in decimal format.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
6mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Probability
Probability is a measure of the likelihood that a particular event will occur, expressed as a number between 0 and 1. In this context, P(L) represents the probability of randomly selecting a subject who writes with their left hand. It is calculated by dividing the number of left-handed individuals by the total number of individuals in the study.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Probability
Complement of an Event
The complement of an event refers to all outcomes in a sample space that are not part of the event. For the event L (selecting a left-handed individual), the complement would be selecting a right-handed individual. Understanding complements is crucial for calculating probabilities and interpreting results in statistics.
Recommended video:

Complementary Events
Data Representation
Data representation involves organizing and displaying data in a way that makes it easy to analyze and interpret. In this case, the data is presented in a table format, showing the number of left-handed and right-handed individuals by gender. This structured format helps in calculating probabilities and understanding the distribution of left-handedness in the sample.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Visualizing Qualitative vs. Quantitative Data

 4:23m
4:23mWatch next
Master Complementary Events with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
