Table of contents
- 1. Intro to Stats and Collecting Data55m
- 2. Describing Data with Tables and Graphs1h 55m
- 3. Describing Data Numerically1h 45m
- 4. Probability2h 16m
- 5. Binomial Distribution & Discrete Random Variables2h 33m
- 6. Normal Distribution and Continuous Random Variables1h 38m
- 7. Sampling Distributions & Confidence Intervals: Mean1h 3m
- 8. Sampling Distributions & Confidence Intervals: Proportion1h 12m
- 9. Hypothesis Testing for One Sample1h 1m
- 10. Hypothesis Testing for Two Samples2h 8m
- 11. Correlation48m
- 12. Regression1h 4m
- 13. Chi-Square Tests & Goodness of Fit1h 20m
- 14. ANOVA1h 0m
2. Describing Data with Tables and Graphs
Histograms
Problem 2.1.23b
Textbook Question
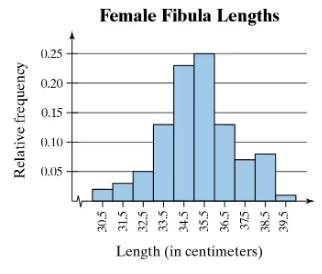
Use the relative frequency histogram to
approximate the greatest and least relative frequencies.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Observe the relative frequency histogram provided. The x-axis represents the length of female fibulas in centimeters, while the y-axis represents the relative frequency.
Step 2: Identify the bar with the greatest height on the histogram. The height of the bar corresponds to the greatest relative frequency. Approximate the value by observing the y-axis scale.
Step 3: Identify the bar with the smallest height on the histogram. The height of the bar corresponds to the least relative frequency. Approximate the value by observing the y-axis scale.
Step 4: Note the range of lengths (x-axis) associated with the bars of greatest and least relative frequencies. This provides additional context for the data distribution.
Step 5: Summarize the findings by stating the approximate greatest and least relative frequencies based on the histogram and their corresponding length ranges.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Related Videos
Related Practice





